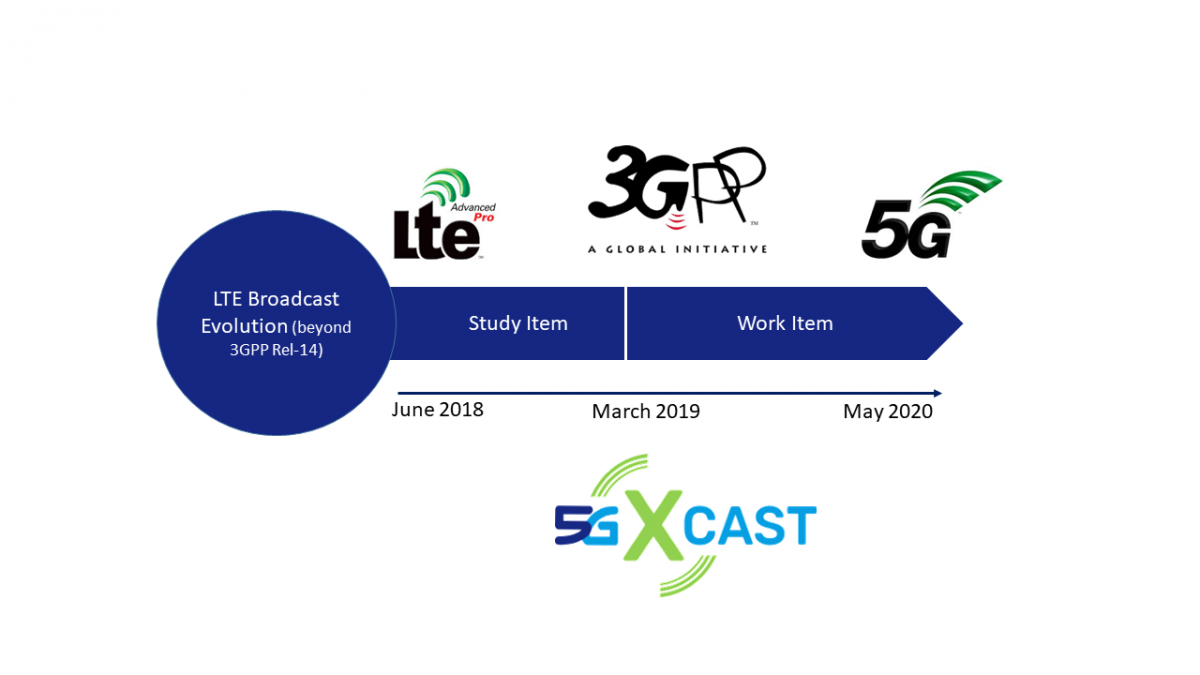
The enhancement of the existing LTE technology to deliver linear TV and radio services to an infinite number of receivers was identified as one of the points to address in 3GPP after the definition of FeMBMS in the latest version of Release 14. As part of the Release 16 framework, 3GPP has started the normative work to further develop LTE-based 5G Terrestrial Broadcast. The solution, which is also known as 5G broadcast, is defined as the 3GPP technology able to deliver audiovisual free-to-air services from one or different transmitters in SFN to multiple receivers on dedicated broadcast infrastructure (e.g. High-Power High-Tower Single Frequency Networks) using the LTE/5G chipset already present in the smartphone to receive linear TV and radio services.
Study Item Phase
3GPP approved the Study on LTE-based 5G Terrestrial Broadcast (RP-181342) during RAN#80 meeting, held in La Jolla (US), June 2018. The objective of the study was to perform a gap analysis to compare the capabilities of LTE FeMBMS Release 14 with the requirements for 5G dedicated broadcast networks specified in TR 38.913. The study item was supported by multiple 5G-Xcast partners such as BBC, British Telecom, EBU, IRT, Nomor, Nokia, One2many and Samsung, together with some Advisory Board members like Cellnex Telecom or the University of the Basque Country.
The normative work related to the Study Item was kicked off during RAN1 #94bis meeting, held in Chengdu (China). During this meeting, the skeleton of TR 36.776 on LTE-based 5G terrestrial broadcast was presented. Our 5G-Xcast partners, BBC, IRT and EBU participated actively by presenting two different contributions on public service requirements (R1-1810319) and scenarios and simulation assumptions (R1-1811588). During the next RAN1 meetings, RAN1 #95 (Spokane, US) and RAN1 #96 (Athens, Greece), different evaluation results were presented and discussed. 5G-Xcast partners BBC, IRT and EBU contributed with two different documents (R1-1812430) and (R1-1902130).
The outcome of the study was captured in TR 36.776, where the main enhancements identified for meeting the 5G requirements were specified: i) to support a more efficient integration of the HPHT (high-power high-tower) broadcast infrastructure for large area SFN coverage and ii) to enable high speed reception from medium-scale SFN areas. Additionally, the numerology mismatch of the cell-acquisition subframe (CAS) was identified and extensively analysed due to the disparity of results related to the different methodologies proposed.
All these aspects were already analysed in 5G-Xcast during the study performed in 5G-Xcast D3.1, last 2018.
Work Item Phase
As a consequence of the work carried out in the Study Item phase, a new Work Item on LTE-based 5G terrestrial broadcast was approved during the RAN#83 plenary meeting held in Shenzhen (China), March 2019. The main objectives of the Work Item are: (i) to specify new numerologies and signalling for the support of fixed and mobile reception in MPMT and HPHT environments, and (ii) enhance (if required) the physical channels and signals conveyed in the CAS. 3GPP specified the work plan for the work item in R1-1904533.
As it happened during the Study Item phase, this WID also received support from a considerable number of 5G-Xcast partners such as British Telecom, BBC, EBU, IRT, Nomor, Nokia, One2Many and Samsung.
BBC, EBU and IRT are expected to keep contributing to the normative work required in this new stage, leveraging the research and technology developed during the last two years in project’s life. During the RAN1#96bis meeting held in Xian (China), our 5G-Xcast partners participated in the initial discussions related to the design of numerologies (around 100us and 400us) and potential improvements in the CAS. In particular, BBC, EBU and IRT presented two different contributions on Network Simulations for the CAS (R1-1905330) and Information for Time Variation Models (R1-1905331).
Further discussions on the numerology design were held during the RAN1 #97 meeting held in Reno, Nevada (US). During the meeting down-selection of numerologies was done in order limit the complexity of the FFT sizes for the numerology close to 400us cyclic prefix. For the numerology of 100us, the benefits in terms of overhead of different RS patterns were evaluated. For the CAS, in order to avoid the modification of the numerologies of the control channels that constitute it, the proposed solutions rely on increasing the aggregation level of the PDCCH or an averaging over PBCH. The lack of specific mechanisms to synchronize control channels in SFN mode are still pending to be resolved. During this meeting BBC, EBU and IRT presented two contributions on Network Simulations for the CAS (R1-1906634) and Spectral Efficiency of New Numerologies for Rooftop Reception (R1-1907093).
Towards next meetings in August, October and November 2019, final agreements on MCS/TBS and RS configurations together with agreements on RRM core requirements are expected to be reached. From February 2020, the final configurations, scenarios and evaluation results will be discussed and agreed before the expected completion date in May 2020.
5G-Xcast impact on standardisation
During the Study Item and Work Item phase, our 5G-Xcast partners have actively contributed to the development of the new LTE-based 5G Terrestrial Broadcast solution, making an impact on the standardisation process by leveraging the use of 5G-Xcast capabilities presented in D3.1 and D3.2. 5G-Xcast has proved itself as a pioneer in the evaluation of FeMBMS and the detection of the necessary changes to develop the next generation of 5G broadcast technology.